Overview Table
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Main Issue | Internet speed fluctuates due to multiple technical and environmental factors |
| Common Causes | Network congestion, ISP throttling, device limitations, weather, routing changes |
| Affected Users | Home users, students, office workers, gamers, remote employees |
| Time Variations | Morning, evening, weekdays, weekends |
| Technical Factors | Bandwidth sharing, server load, DNS routing |
| External Factors | Weather, infrastructure issues, maintenance |
| User Control | Partial control through device optimization and plan upgrades |
| ISP Role | Major influence through infrastructure, policies, and traffic management |
| Long-Term Solution | Better plans, stable hardware, optimized usage habits |
Introduction
Many people notice that their internet speed is not consistent every day. One day the connection feels fast and smooth, while the next day it becomes slow, unstable, or frustrating. This daily variation in internet speed is a common experience across homes, offices, and even mobile networks. Despite paying for a fixed Internet Speed plan, users often wonder why the promised speed is not delivered consistently.
Internet speed changes are not caused by a single issue. Instead, they result from a combination of technical, environmental, and usage-related factors. Internet Speed connectivity relies on a complex network of infrastructure, servers, cables, wireless signals, and software systems. Even small changes in any of these components can impact speed and performance.
This article explains in detail why internet speed changes every day, covering network congestion, ISP behavior, device limitations, environmental influences, and user habits. Understanding these factors helps users make better decisions and improve their overall Internet Speed experience.

Understanding How Internet Speed Works
Internet speed refers to how fast data travels between your device and the Internet Speed. It is usually measured in megabits per second and includes download speed, upload speed, and latency. Download speed affects how quickly web pages load or videos stream, while upload speed matters for sending files or video calls. Latency determines how responsive the connection feels.
Your Internet Speed connection does not work in isolation. Data travels from your device to a router, then to your Internet Service Provider, through multiple servers and network routes, and finally to the destination server. Each step introduces potential delays or limitations. Since these routes and network conditions change constantly, internet speed can vary from day to day.
Network Congestion
What Network Congestion Means
Network congestion occurs when too many users are trying to access the Internet Speed at the same time. Internet bandwidth is shared among multiple users, especially in residential areas. When demand exceeds available capacity, speed slows down for everyone connected to that network segment.
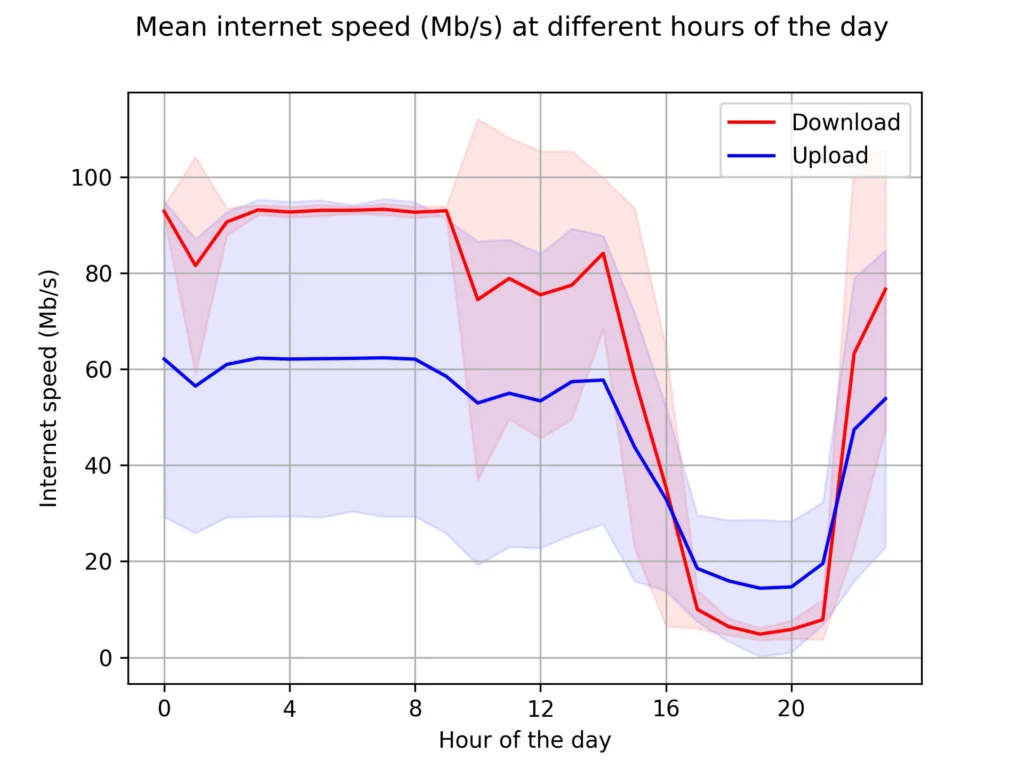
Peak Hours and Daily Speed Drops
Internet speed often decreases during peak hours such as evenings and weekends. During these times, people stream videos, attend online meetings, play games, and browse social media simultaneously. This increased demand puts pressure on local network infrastructure, leading to slower speeds.
Neighborhood-Level Impact
In many areas, multiple homes share the same network node. If several households are heavily using the Internet Speed at the same time, the available bandwidth gets divided, causing noticeable slowdowns. On quieter days or during off-peak hours, speed improves because fewer users are competing for bandwidth.
Internet Service Provider Traffic Management
Bandwidth Allocation Policies
Internet Speed Service Providers manage network traffic to ensure stability. They may prioritize certain types of data while limiting others during high-traffic periods. This practice can cause speed fluctuations depending on the type of activity you are performing.
Throttling and Fair Usage Policies
Some ISPs reduce speeds temporarily if a user exceeds a certain data threshold. This is often referred to as throttling. Even unlimited plans may include fair usage limits that affect speed during heavy usage days.
Infrastructure Limitations
ISPs continuously upgrade their networks, but infrastructure limitations still exist in many regions. Older cables, outdated equipment, or limited capacity can cause inconsistent performance from one day to another.
Distance from Servers and Routing Changes
Data Routing Variations
Internet Speed data does not always follow the same path every day. Network routing can change based on traffic conditions, server availability, or maintenance activities. A longer or more congested route can slow down your connection even if your local network is stable.
Server Load Differences
The performance of websites and online services also affects perceived internet speed. If a server is under heavy load, responses will be slower regardless of your Internet Speed plan. On different days, the same website may perform differently due to varying server demand.
Device and Hardware Factors
Router Performance
Routers play a crucial role in internet speed. Over time, routers can become overloaded due to continuous operation, outdated firmware, or internal memory limitations. A router that performs well one day may struggle the next if it is handling too many connections.
Device Limitations
Older smartphones, laptops, or computers may not support newer Wi-Fi standards or higher speeds. Background processes, software updates, and malware can also reduce performance on certain days.
Number of Connected Devices
The more devices connected to a network, the more bandwidth is divided. Smart TVs, security cameras, gaming consoles, and smartphones all consume data. Daily changes in device usage patterns can affect overall speed.
Wi-Fi Interference and Signal Quality
Wireless Interference
Wi-Fi signals can be affected by interference from other networks, electronic devices, and physical obstacles. Neighboring Wi-Fi networks may operate on the same channel, causing congestion and speed drops.
Physical Barriers
Walls, furniture, and building materials can weaken Wi-Fi signals. Changes in device location or environmental conditions can alter signal strength from day to day.
Frequency Band Differences
Modern routers use both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The 2.4 GHz band travels farther but is more crowded, while the 5 GHz band is faster but has shorter range. Automatic switching between these bands can cause speed variations.
Weather and Environmental Conditions
Impact of Weather on Infrastructure
Weather conditions such as rain, storms, and high humidity can affect internet infrastructure, especially in areas using wireless or cable-based connections. Moisture can interfere with signal transmission and cause temporary slowdowns.
Temperature Effects
Extreme heat can impact networking equipment, leading to reduced efficiency or temporary failures. Cold temperatures can also affect outdoor cables and connectors.
Software Updates and Background Processes
Automatic Updates
Operating systems, applications, and devices often download updates automatically. These updates may occur on different days, consuming bandwidth and reducing available speed for other tasks.
Cloud Synchronization
Cloud services sync files in the background. Large uploads or downloads can slow down internet performance without the user realizing it.
Type of Internet Connection
Fiber, Cable, DSL, and Mobile Differences
Different types of internet connections behave differently. Fiber connections offer consistent speeds, while cable and DSL connections are more prone to congestion. Mobile networks depend heavily on signal strength and tower load, leading to daily fluctuations.
Shared Medium Limitations
Cable and mobile networks are shared among many users. Increased usage in your area directly impacts speed consistency.
Time-Based Usage Patterns
Weekday vs Weekend Differences
Internet usage patterns change between weekdays and weekends. Offices, schools, and remote workers contribute to daytime traffic, while entertainment usage peaks in the evening.
Seasonal Changes
During holidays or exam seasons, internet demand increases, causing slower speeds. Seasonal factors can create noticeable changes over time.
Security and Malware Issues
Malware Activity
Malware can consume bandwidth by sending data without the user’s knowledge. This can cause sudden speed drops that vary from day to day.
Unauthorized Access
If someone gains access to your Wi-Fi network, they may use your bandwidth, reducing speed unexpectedly.
ISP Maintenance and Network Issues
Scheduled Maintenance
ISPs perform regular maintenance to improve service quality. During or after maintenance, temporary slowdowns may occur.
Unexpected Outages
Hardware failures, cable damage, or technical issues can cause temporary speed changes that resolve on their own.
User Behavior and Internet Habits
Streaming Quality Settings
Video streaming platforms adjust quality automatically based on network conditions. Higher resolution streaming consumes more bandwidth and can impact speed for other activities.
Download and Upload Activities
Large file downloads, backups, or uploads can significantly reduce available bandwidth, causing slower speeds on certain days.
How to Improve Daily Internet Speed Consistency
Optimize Router Placement
Placing the router in a central, elevated location reduces signal interference and improves coverage.
Upgrade Hardware
Using modern routers and devices that support the latest standards improves performance and stability.
Manage Connected Devices
Disconnect unused devices and limit background activities to free up bandwidth.
Monitor Usage Patterns
Understanding when and how internet usage peaks helps plan activities during off-peak hours.
Long-Term Solutions for Stable Internet Speed
Upgrading to a higher-speed plan, switching to fiber if available, and choosing a reliable ISP can significantly improve consistency. Regularly updating hardware and securing the network also play important roles in maintaining stable internet performance.
Conclusion
Internet speed changes every day because it depends on many interconnected factors rather than a single fixed system. Network congestion, ISP policies, routing changes, device performance, Wi-Fi interference, environmental conditions, and user behavior all contribute to daily variations. While some factors are beyond user control, many issues can be minimized through better hardware, optimized settings, and informed usage habits.
Understanding why internet speed fluctuates helps set realistic expectations and empowers users to improve their connection quality. By addressing controllable factors and working with reliable service providers, users can achieve a more stable and satisfactory internet experience over time.

